In the quest for sustainable and efficient building management, Building Automation Systems (BAS) have emerged as a cornerstone technology. These systems offer an integrated approach to controlling and optimizing building operations, significantly contributing to energy efficiency and operational cost savings.
Centralized Control and Optimization
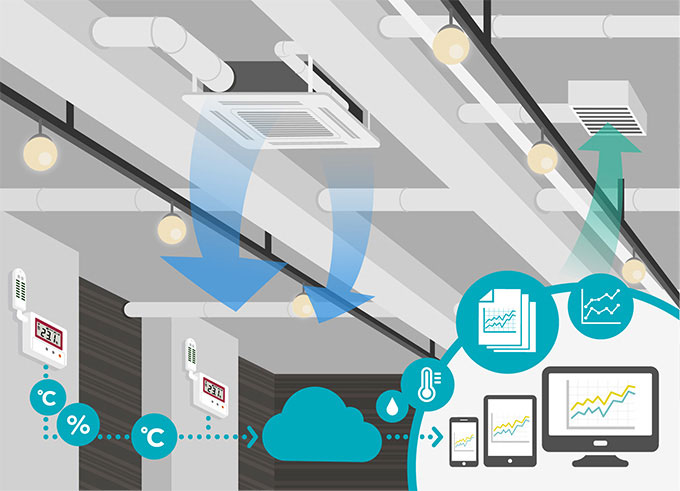
Building automation primarily revolves around the centralized control of a building’s HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), lighting, and other systems. By leveraging advanced technologies like IoT sensors and smart controls, BAS can intelligently adjust settings based on real-time data, such as occupancy levels and environmental conditions.
Substantial Savings through Smart Systems
One of the most impactful benefits of BAS is the substantial energy savings it offers. For instance, smart HVAC systems can dynamically adjust heating and cooling based on the occupancy of different zones in a building. This not only ensures optimal comfort levels but also avoids energy wastage in unoccupied areas. Similarly, automated lighting systems equipped with motion sensors and daylight harvesting capabilities ensure that lights are used efficiently and only when needed.

Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Moreover, BAS facilitates continuous monitoring and data analysis, enabling facility managers to identify inefficiencies and implement targeted improvements. This ongoing process of optimization leads to a consistently high level of energy efficiency. The systems can also provide predictive maintenance alerts, preventing equipment failures that could lead to increased energy usage and costly repairs.
However, the implementation of BAS is not without its challenges. The initial cost can be significant, and integrating these systems into existing buildings may require substantial retrofitting. Additionally, the complexity of BAS necessitates skilled personnel for operation and maintenance.
A Practical Solution for Sustainability
Despite these challenges, the benefits of building automation in terms of energy conservation and operational efficiency are undeniable. In an era where sustainability is a priority, BAS stands out as a powerful tool for reducing the environmental impact of buildings. It not only aligns with global green initiatives but also offers a practical solution for reducing operational costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, building automation systems represents a major leap forward in energy management for facilities. By embracing this technology, facility managers can significantly contribute to creating more sustainable, efficient, and cost-effective buildings.







